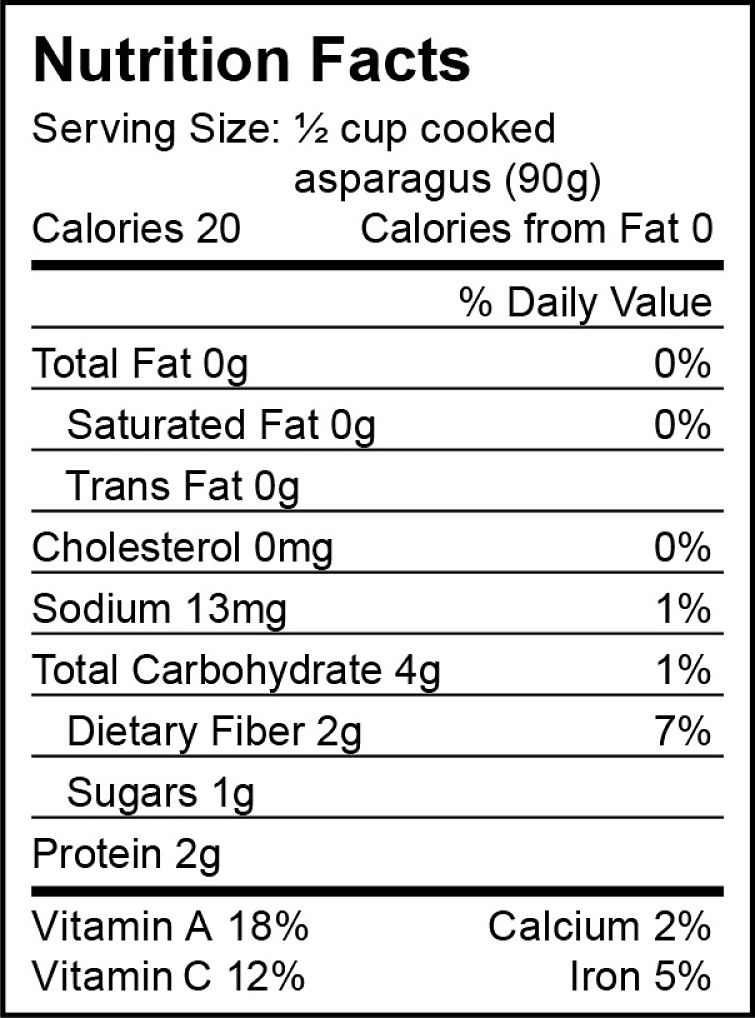
Health Benefits Asparagus, Nutrition Facts and Cooking Tips
Freshly cooked asparagus has an outstanding array of health benefits showcased by its nutritional facts.
Asparagus is an excellent source of folate, fiber, vitamins A, C, E and K, as well as several minerals.
Asparagus has its own family (Asparagaceae) and is broadly related to garlic, leeks and onions (family Amaryllidaceae). The edible parts are the spear shaped shoots that have a compact and pointed head. The main photosynthesizing function in this family is the stems or shoots with the leaves reduced to small bract-like structures. These shoots are picked as they appear each day and light exposure is minimized to keep them cream to light green in color. Older shoots are dark green to purple in color.
Although it's available right throughout the year, fresh asparagus is usually at its best in Spring. The shoots are harvested when about 6 to 8 inches long (15 cm).
This article summarizes the health benefits of asparagus and includes the asparagus nutritional information in a table.
It also includes a table comparing the nutrients in asparagus with alternative green vegetables such as cooked green snap beans, green peas, okra and cabbage.

Health Benefits of Asparagus
The two tables below summarise the nutritional data for asparagus in relation to other vegetables.
- Asparagus is an alkaline food which is relatively rich in protein but low in calories and carbohydrates. There are 2gm of protein in 100gm of asparagus which is higher than for green sap peas, okra and cabbage, though there is more protein in green peas. Asparagus only has 22 calories for 100g and this is the lowest for the other four vegetables.
- Asparagus is a good source of dietary fiber with 2gm in every 100g of asparagus, equivalent to the fiber in green snap beans, okra and cabbage.
- Asparagus has more Vitamin A than the other four vegetables and 100g of asparagus provides about 20% of the daily allowance.
- Asparagus is relatively rich in niacin, phosphorus and has very low sodium levels.
- Asparagus is a rich source of the amino acid called asparagine, that plays a role in the process of removing waste from the body.
- Fresh asparagus spears provide an excellent source of anti-oxidants such as zeaxanthin, carotenes, lutein and crypto-xanthins.
- Fresh asparagus are rich in folates and other B group vitamins. A serving of 100 g of asparagus spears provide about 54 micro g or 14% of recommended daily allowance of folic acid.
- Asparagus are also a rich source if Vitamin B group compounds such as thiamin, niacin, vitamin B-6 (pyridoxine), riboflavin and pantothenic acid that support many of the metabolic acticities of the cells
- Asparagus are an excellent source of vitamin K, with 100g providing about 35% of the recommended daily allowance. Vitamin K has crucial role in maintaining bone health.
- Asparagus is a very good source of minerals especially iron, potassium, manganese and copper.
- Asparagus is very easy to prepare by steaming and in the microwave. The faster cooking means that less nutrients are lost in the boiling water. Asparagus can also be grilled ad stirfried so that no immersion in water is required.
Comparison of Nutrients in Asparagus with other Vegetables
|
Serving Size (100gm)
|
Asparagus (cooked)
|
Green snap beans (boiled
|
Peas, green, cooked, boiled
|
Okra, cooked, boiled
|
Cabbage, cooked boiled
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Calories
|
22
|
35.2
|
83.8
|
22.5
|
23.0
|
|
Total Fat (gm)
|
0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
|
Cholesterol (gm)
|
0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
0.0
|
|
Sodium (mg)
|
14
|
0.8
|
3.1
|
6.3
|
8.0
|
|
Total Carbohydrate (gm)
|
4
|
8.0
|
15.6
|
5.0
|
5.5
|
|
Dietary Fiber (gm)
|
2
|
3.2
|
5.6
|
2.5
|
1.9
|
|
Sugars (gm)
|
1
|
1.6
|
5.6
|
2.5
|
2.8
|
|
Protein (gm)
|
2
|
1.6
|
5.6
|
1.3
|
1.3
|
|
Vitamin A (percent daily allowance)
|
20%
|
14%
|
16%
|
6%
|
2%
|
|
Calcium (percent daily allowance)
|
2%
|
5%
|
3%
|
7%
|
5%
|
|
Vitamin C (percent daily allowance)
|
1%
|
1%
|
1%
|
1%
|
4%
|
|
Iron (percent daily allowance)
|
5%
|
4%
|
9%
|
1%
|
1%
|
Buying and Preparing Asparagus
When selecting asparagus to buy, choose firm, straight stalks that do not droop when picked up and have tight, firm tips. The cream and light green spears have a more delicate flavor but have less nutrients than the darker green spears. Always try to eat asparagus on the day of purchase. A bunch of spears can be kept at room temperature by placing in a glass of water. Otherwise, wrap the spears in tightly-wrapped plastic and store in the refrigerator for up to three days.
Cooking Tips for Asparagus
- When cooking asparagus, always try to lightly steam the spears rather than boiling as this preserve the nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Always leave them just cooked, to avoid the limp and unexciting over-cooked spears that lack texture and flavor.
- Avoid cooking asparagus spears in iron pots as asparagus contains tannins that can react with the iron and discolor the asparagus spears.
- Roast, grill or stir-fry asparagus as these waterless methods preserve the nutrients and antioxidants power of asparagus.
- Asparagus spears can be rather bland by themselves and are best served with a sauce or cheese. Some serving suggestions are citrus hollandaise sauce, parmesan or pecorino cheese, melted butter, or a light drizzle of soy sauce.
- Grilled or barbecued asparagus is truly a treat as the smokey flavors are absorbed into the spears, which should be left firm and not overcooked. Drizzle with some lemon or orange juice over the spears while cooking and add, Cajun seasoning or fresh parmesan cheese at the very end of the cooking to make a delightful, quick appetizer. Grilling asparagus stalks smeared with macadamia nut oil and serving with sauteed spring onions makes a wonderful appetizer.
- Chopped asparagus can be added to all sorts of stir fry dishes and also to homemade pasta sauce and added to pizza toppings.
- You can also roast or bake asparagus in an oven preheated to about 450 degrees F (230 degrees C) for about 4 to 6 minutes, until just tender. Roasting asparagus is easy to do and the flavors are sensational. Just sprinkle the spears with salt, pepper and you favorite spices. Or you can layer thin slices of ham or prosciutto before baking.
See => Cooking Fresh Asparagus - How to Fry, Roast, Steam, Microwave and Grill
Nutrition Facts for Asparagus
|
100g raw asparagus
|
Nutrient Value
|
% recom. Daily allowance
|
|---|---|---|
|
Energy
|
20 Cal
|
1%
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
3.38 g
|
2.5%
|
|
Protein
|
2.20 g
|
4%
|
|
Total Fat
|
0.12 g
|
0.5%
|
|
Cholesterol
|
0 mg
|
0%
|
|
Dietary Fiber
|
2.1 g
|
5.5%
|
|
Vitamins
|
|
|
|
Folates
|
52 mcg
|
13%
|
|
Niacin
|
0.98 mg
|
6%
|
|
Pantothenic acid
|
0.27mg
|
5%
|
|
Pyridoxine
|
0.09 mg
|
7%
|
|
Riboflavin
|
0.14 mg
|
11%
|
|
Thiamin
|
0.14 mg
|
12%
|
|
Vitamin C
|
5.6 mg
|
9%
|
|
Vitamin A
|
756 IU
|
25%
|
|
Vitamin E
|
1.13 mg
|
7.5%
|
|
Vitamin K
|
41.6 mcg
|
35%
|
|
Electrolytes
|
|
|
|
Sodium
|
2 mg
|
|
|
Potassium
|
202 mg
|
4%
|
|
Minerals
|
|
|
|
Calcium
|
24 mg
|
2.5%
|
|
Copper
|
0.19 mg
|
21%
|
|
Iron
|
1.14 mg
|
14%
|
|
Magnesium
|
14 mg
|
1%
|
|
Manganese
|
0.16 mg
|
7%
|
|
Phosphorus
|
52 mg
|
7.5%
|
|
Selenium
|
2.3 mcg
|
4%
|
|
Zinc
|
0.54 mg
|
5%
|
|
Phyto-nutrients
|
|
|
|
Carotene-beta
|
449 mcg
|
|
|
Carotene-alpha
|
9 mcg
|
|
|
Lutein-zeaxanthin
|
710 mcg
|
|