Health Benefits of Ginger - Nutritional Facts, and Dietary, Medicinal Benefits
Fresh ginger root is renowned for its culinary benefits as a Asian food ingredient, and as a dietary supplement.
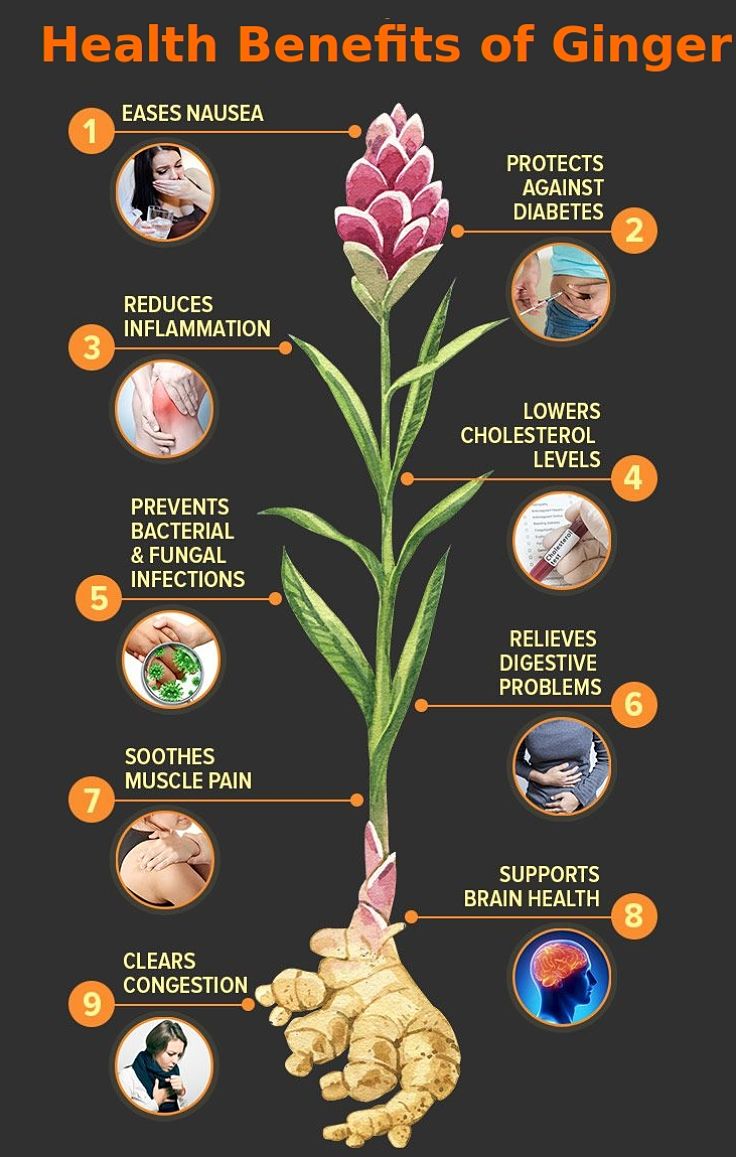
Ginger also has an outstanding array of medicinal benefits for maintaining good health and well being.
Ginger has a long-standing tradition in ancient Indian and Chinese medicines and is increasingly being use in many home remedies.
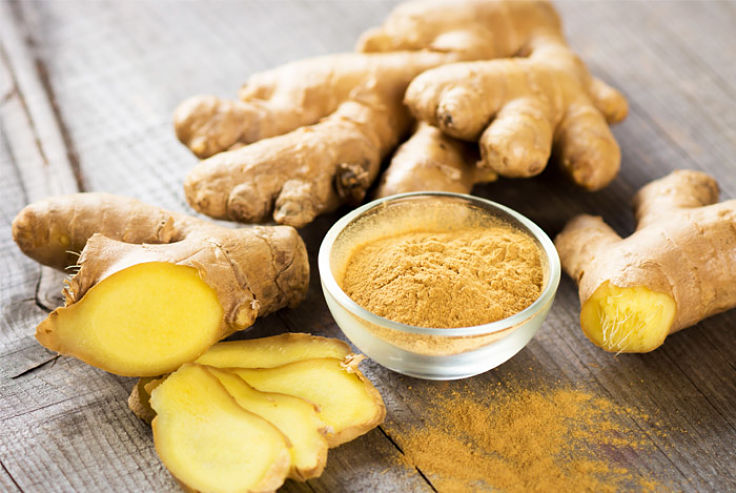
Ginger root is the rhizome of small herb plant that grows underground. Ginger is believed to have originated in the Himalayan area in Southeast Asia.
Ginger is now widely grown commercially all over the world including India, Fiji, Jamaica, Indonesia and Australia.
The ginger plant reaches a height or about 3 feet (1 meter) and features thin grass-like long dark green leaves and when mature bears small yellow flowers.
This article reviews the health benefits and uses of fresh ginger root both in food, as a supplement and its medicinal values for various home remedies.
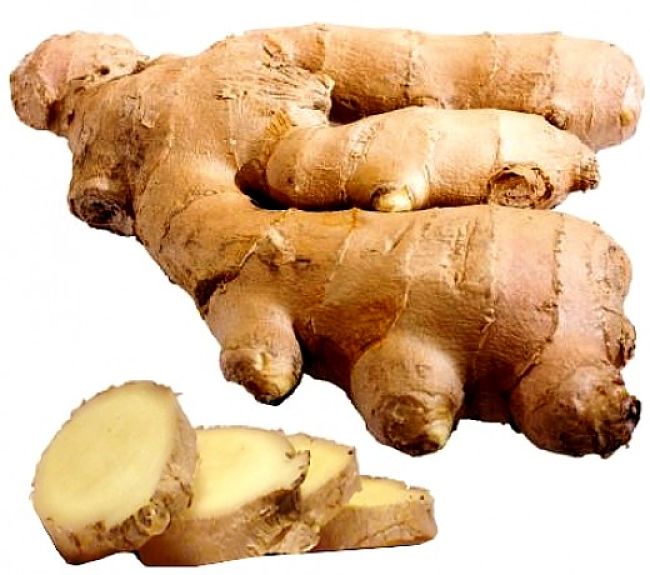

Ginger plants can be easily grown in your home garden or in pots so that you will always have fresh roots available as needed.
When buying ginger to cook with always choose fresh ginger root, rather than the dried forms since fresh ginger has better quality and flavor. Many of the substances that provide the benefits, such as the gingerols are volatile and are eliminated when ginger is dried.
When looking for fresh ginger the roots should feel heavy and stout and not shown any sign of drying out. Also choose roots that are free from dark spots or mold.
Larger pieces many be less wasteful to peel and prepare, but they contain more fibers. Fresh root can be kept in the refrigerator a few weeks to a month.
The freshly dug rhizome has silver gray, cream or light brown outer skin color. When cut the ginger flesh is colored creamy white, red or yellow depending on the variety.
The characteristic spicy, pungent aroma arises from the unique essential oils oil and phenolic compounds the ginger plant produces such as shogaols and gingerols.
Culinary Benefits of Ginger Root
See the table for details showing the nutritional facts for 100 g of fresh ginger root.
Fresh Ginger root has few calories ( 80 calories per 100 g) and contains no cholesterol. Ginger is a rich source of B group vitamins such as pyridoxine (vitamin B6; 12% of daily allowance), pantothenic acid (vitamin B5; 4% of daily allowance). It also has moderate levels of dietary fiber (2 g per 100 g)
One hundred grams of ginger also contains moderate amount of minerals like potassium (9% of daily allowance), manganese (10% 0f daily allowance), magnesium( 11% of daily allowance), iron and copper. Potassium is an important in maintaining cell and body fluids. It helps control heart rate and blood pressure in association with sodium.
Medicinal Benefits of Ginger Root
Ginger has been widely used for centuries for medicinal purposes because of its anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, calming and anti-flatulent properties. Ginger root is used for a variety of home remedies such as motion sickness, vomiting associated with pregnancy and general nausea and various inflammatory illnesses. Various medicinal trials have shown the effectiveness of ginger for treatment of motion sickness and may provide more relief than the various prescribed drugs. Ginger has been shown to be effective in relieving all the symptoms linked with motion sickness including nausea, vomiting, dizziness and cold sweating.
Ginger's powerful anti-inflammatory properties is linked with gingerols. Many people with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis get relief from pain and extra mobility when they consume ginger regularly. Gingerols have also been shown may also inhibit the growth of human colorectal cancer cells in various published research studies.
Ginger also helps to maintain the immune system and helps promote sweating, which can relieve the symptoms of colds and flu.
Culinary Uses for Ginger Root
- Fresh root has pungent spicy flavor and peppery taste that enhances many South-East Asian, Chinese, Indian and West Indies dishes. Some people prefer the ginger to be finely diced so the flavor blends with the other ingredients. Others like to have small chunks of ginger in the dish to provide burst of aroma and flavor. To keep the fragrance and flavor and to retain the volatile oils in the dish it is generally best to add the ginger at the last minute.
- For stir fry dishes, finely diced ginger is often added to marinates for beef, pork and chicken.
- Ginger is also used in the preparation of various pickles.
- Fresh Ginger root is also added to a variety of spicy snacks, cakes, biscuits, cookies slices, candies and the famous unique gingerbread. Fresh ginger provides more aroma and flavor that dried ginger.
- Fresh Ginger is also used to make homemade ginger beer and ginger wine.
- Add an interesting touch to rice by sprinkling grated ginger and sesame seeds through it when half cooked.
- Fresh grated ginger can be combined with olive oil, soy sauce and garlic to make a wonderful homemade salad dressing.
- Ginger and orange juice provide a flavor burst to pureed or mashed sweet potatoes.
- Ginger combined with soy sauce, garlic oil and various spices makes a wonderful coating for roast meat such as pork and chicken.
Nutritional Facts for Fresh Ginger Root 100 g
|
Serving 100g fresh ginger root
|
Nutrient Value
|
Percent of recommended daily allowance
|
|---|---|---|
|
Energy
|
80 Cal
|
4%
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
17.77 g
|
14%
|
|
Protein
|
1.82 g
|
3%
|
|
Total Fat
|
0.75 g
|
3%
|
|
Cholesterol
|
0 mg
|
0%
|
|
Dietary Fiber
|
2.0 g
|
5%
|
|
Vitamins
|
|
|
|
Folates
|
11 mcg
|
3%
|
|
Niacin
|
0.750mg
|
4%
|
|
Pantothenic acid
|
0.2 mg
|
4%
|
|
Pyridoxine
|
0.16 mg
|
12%
|
|
Vitamin A
|
0 IU
|
0%
|
|
Vitamin C
|
5 mg
|
8%
|
|
Vitamin E
|
0.26 mg
|
2%
|
|
Vitamin K
|
0.1 mcg
|
0%
|
|
Vitamin B6
|
0.1 mg
|
1%
|
|
Electrolytes
|
|
|
|
Sodium
|
13 mg
|
1%
|
|
Potassium
|
415 mg
|
9%
|
|
Minerals
|
|
|
|
Calcium
|
16 mg
|
2%
|
|
Copper
|
0.1 mg
|
|
|
Iron
|
0.60 mg
|
7%
|
|
Magnesium
|
43 mg
|
11%
|
|
Manganese
|
0.23 mg
|
10%
|
|
Phosphorus
|
34 mg
|
5%
|
|
Zinc
|
0.34 mg
|
3%
|
|
Potassium
|
84 mg
|
4%
|